The project introduces new optical techniques in veterinary oncology, greatly simplifying histological sample preparation and allowing veterinarians to obtain histopathology (HP) results in near real time. Currently, standard HP analysis takes several days to obtain clear surgical margins and can only survey a limited area. The new method will allow unlabelled HP analysis of tumour types and the recognition of clear surgical margins in the most common canine and feline tumours: soft tissue sarcomas and mast cell tumours. Our proposed innovation concerns autofluorescence and Raman spectral band imaging and the introduction of optical coherence tomography (OCT) for histological pattern recognition.
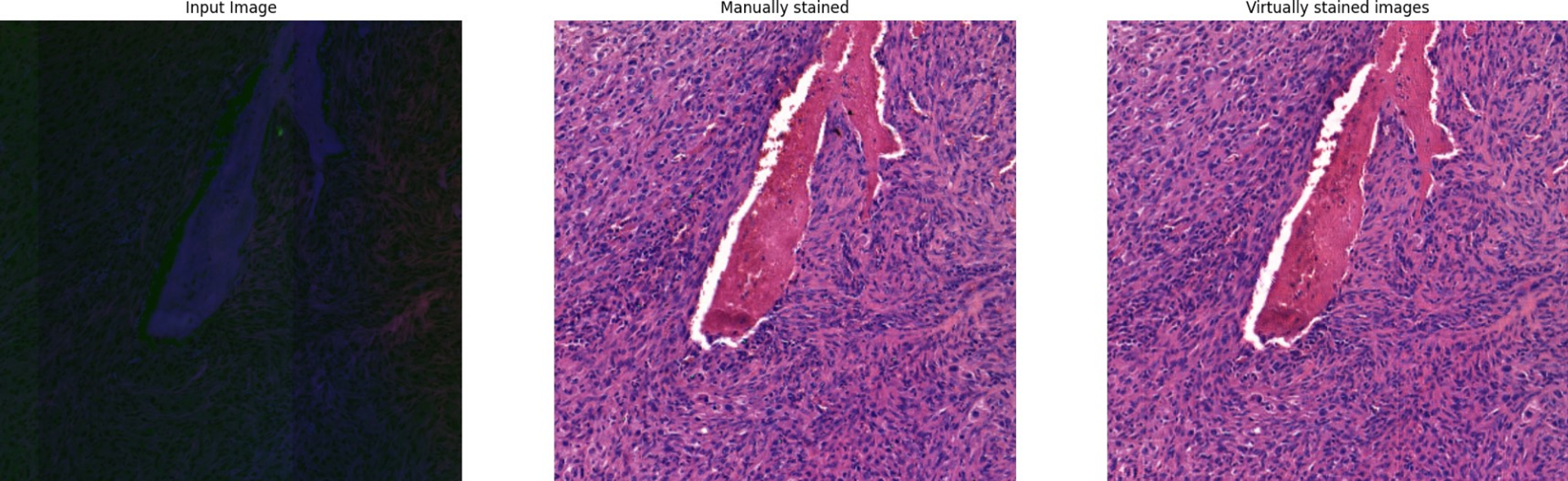
EDI team investigates image translation approaches for virtual image staining. Generative adversarial networks (GANs) and generative diffusion models are adapted, enhanced and trained to produce stained histological images from unstained ones, replacing the long and labor-intensive manual staining process. In addition to the AI models that perform virtual staining or image translation, EDI develops and applies the necessary image pre-processing algorithms that improve the staining result.
The imaging with AI-based virtual staining techniques proposed in the project will improve the automated histological analysis of unstained tissue ex vivo, allowing the detection of incomplete histological boundaries at the microscopic level. These methods are to be incorporated in a prototype to be made available in Latvian veterinary oncology clinics.